

In this section, we will look at the working of the NumPy stack() function for two one-dimensional NumPy arrays. The numPy stack() function returns a NumPy array.
By default, np.stack() stacks arrays along the 0th dimension (rows). The parameters that the NumPy stack() function takes in are: Cheatsheet for Python numpy reshape, stack, and flatten (created by Hause Lin and. The syntax for numpy stack() function is: The numPy concatenate() function is also used to combine two or more arrays, but by using numPy stack(), we can combine arrays along a new axis.
#NP STACK PYTHON SERIES#
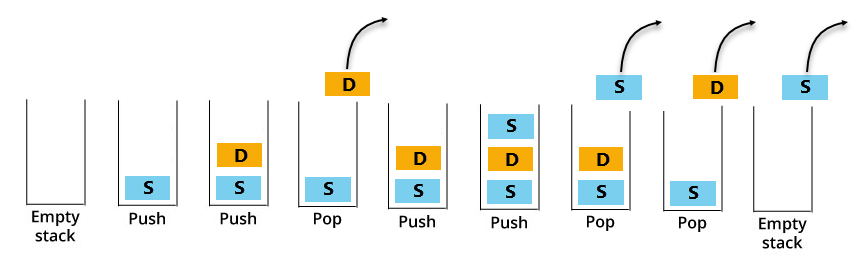
The numpy stack() function is used to combine a series of arrays along a new axis. The first book to be taken off the stack would be the one that has been there most recently. The first book stacked will be the last to be removed from the stack. Conversely, the element that is inserted into the stack recently is the first one to be popped out.Ī stack in the actual world would be a collection of books. To sum it up, the element that enters the stack in the beginning, is the last one to be popped out. This order is the Last In First Out order.
#NP STACK PYTHON CODE#
#NP STACK PYTHON SOFTWARE#
Just like NumPy, data structures are equally important for a Software Developer.ĭata structures are a particular way of arranging information on a computer in a specialized style so that it may be processed, stored, and retrieved efficiently. It greatly simplifies our jobs as developers.
For details, refer to the official documentation below. Other methods like np.r_ and np.c_ will not be discussed here. In most cases, np.concatenate() and np.stack() can handle your needs, but it is helpful to remember np.block(), np.vstack(), and np.hstack(), particularly for 2D arrays. For example, np.concatenate() is used to concatenate 2D arrays vertically and horizontally, while np.stack() is used to stack 2D arrays to create a 3D array. Np.concatenate() concatenates along an existing axis, whereas np.stack() concatenates along a new axis.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
